Describir
- Introducción
- ¿Por qué los campos deportivos necesitan... Fotosensores?
- ¿Cuáles son los beneficios clave de Interruptores de fotocélula ¿en iluminación deportiva?
- ¿Dónde están? Sensores fotoeléctricos ¿Lo más útil en la iluminación de campos deportivos?
- ¿Qué especificaciones técnicas debes buscar en una fotocélula de iluminación deportiva?
- ¿Cómo hacer? Sensores de fotocélula de luz ¿Mejorar los sistemas de iluminación inteligente?
- ¿Cuál es el futuro de? Controladores de alumbrado público ¿en recintos deportivos inteligentes?
- Palabras finales
Los campos deportivos exigen una iluminación fiable para garantizar el rendimiento y la eficiencia energética. Pero ¿cómo pueden estos sistemas funcionar correctamente sin un control manual constante?
La respuesta está en fotocontroles. A interruptor de sensor de luz Detecta los niveles de luz natural y gestiona automáticamente el encendido y apagado de las luces. Esto las hace vitales para los deportes modernos. control de iluminaciónDesde pequeños campos escolares hasta estadios profesionales, las fotocélulas mantienen las operaciones inteligentes y sostenibles.

¿Por qué los campos deportivos necesitan... Fotosensores?
Las instalaciones deportivas modernas deben equilibrar la visibilidad con un funcionamiento eficiente. Una iluminación deficiente puede provocar:
- Errores del jugador
- Accidentes de espectadores
- Riesgos de seguridad
De hecho, los estadios profesionales requieren iluminación instantánea y de alta calidad para mantener los cronogramas de los partidos y los estándares de transmisión.
El sensor de fotointerruptor Funcionan como los ojos de un sistema de iluminación exterior. Miden continuamente la luz ambiental. Cuando la luz desciende por debajo de un umbral, indican a las luminarias que se enciendan; al volver la luz del día, las apagan.
El papel de Sensores fotoeléctricos en automatización de iluminación
- Actúan como controladores del anochecer al amanecer. Esto reemplaza la conmutación manual o temporizada con detección de luz en tiempo real.
- Se integran fluidamente con los sistemas de iluminación inteligente. Esto constituye la base para el control de zonas o las estrategias de iluminación adaptativa.
- Reducen la dependencia de temporizadores programados que pueden desalinearse con los horarios cambiantes de salida y puesta del sol.
¿Cuáles son los beneficios clave de Interruptores de fotocélula ¿en iluminación deportiva?
A continuación, presentamos un vistazo rápido a las 5 principales ventajas de usar sensores de fotocélula de luz En la iluminación de campos deportivos:
Automatización inteligente
El interruptor de sensor de luz exterior Detecta cambios en la luz natural en tiempo real. Activa el encendido de las luminarias sin intervención humana. Esto elimina errores de programación y garantiza que las luces funcionen exactamente cuando se necesitan.
Ahorro de energía
Al apagar las luces durante los períodos de mayor luminosidad, las fotocélulas reducen drásticamente el desperdicio de energía. De hecho, controles de iluminación (incluidas las fotocélulas) pueden reducir el consumo de energía hasta en hasta 30–40 % en aplicaciones en áreas exteriores.
Seguridad mejorada
Los campos deportivos deben estar bien iluminados antes de que oscurezca por completo. sensores fotoeléctricos Garantizar una transición fluida. Esto elimina los desmayos repentinos y protege a los atletas, al personal y a los espectadores.
Bajo mantenimiento
Dado que la iluminación se enciende y apaga automáticamente, se requiere menos supervisión manual. El menor número de horas de funcionamiento también prolonga la vida útil del LED al reducir el estrés térmico y eléctrico.
Flexibilidad de integración
Moderno interruptores de fotocélula Pueden interactuar con DMX, temporizadores, sistemas de automatización de edificios y plataformas IoT. Esto permite el control inteligente de escenas (por ejemplo, para entrenamiento, competición o modo de espera). Al actuar como "disparadores de nivel de luz" básicos, mejoran la automatización de la iluminación LED sin necesidad de un cableado complejo.
¿Dónde están? Sensores fotoeléctricos ¿Lo más útil en la iluminación de campos deportivos?
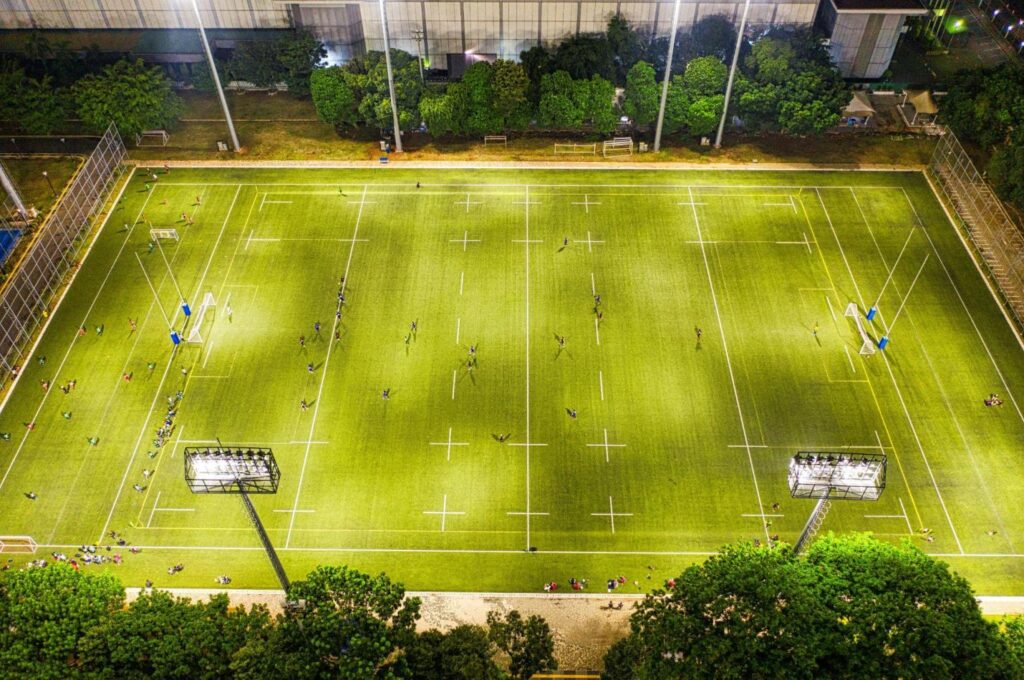

Luces LED de exterior con fotocélulas Brillan en diversos entornos donde la iluminación exterior debe adaptarse automáticamente. A continuación, se presentan tres áreas principales donde su impacto es significativo.
Campos escolares
Los campos deportivos escolares se enfrentan a cambios estacionales: la hora del amanecer y del atardecer cambia. Las fotocélulas ajustan los horarios de iluminación sin necesidad de reinicios manuales. Garantizan que los entrenamientos siempre se realicen con una iluminación segura. Cuando los estudiantes salen tarde en días nublados, el sistema sigue activando las luces antes del anochecer.
Centros deportivos comunitarios
Estos lugares suelen tener largas jornadas y múltiples actividades. Sensores de alumbrado público Evitar el desperdicio de iluminación diurna cuando la luz natural es suficiente.
Combinados con reflectores LED, reducen las facturas de energía de todo el complejo. Se requiere menos supervisión manual, lo que facilita el mantenimiento a los administradores de la comunidad.
Estadios profesionales
En este nivel, la iluminación no se trata solo de visibilidad, sino también de espectáculo, sincronización y control preciso. En los estadios:
- Las fotocélulas alimentan datos de luz ambiental de referencia a los sistemas inteligentes.
- Los sistemas de control de iluminación que utilizan DMX ajustan las escenas (por ejemplo, calentamiento, juego, cierre) según el cronograma y la luz detectada.
- Se integran en plataformas IoT, permitiendo efectos de iluminación dinámicos y control de zonas (tribunas, terreno de juego, vestíbulos).
¿Qué especificaciones técnicas debes buscar en una fotocélula de iluminación deportiva?
A continuación se muestra una tabla concisa de especificaciones recomendadas para fotocélulas de grado deportivo:
| Parámetro | Valor sugerido/rango |
| Sensibilidad (Encendido) | 10 a 20 lux |
| Sensibilidad (Apagado) | 30 a 50 lux |
| Protección (clasificación IP) | IP65 o superior (sellado contra polvo y agua) |
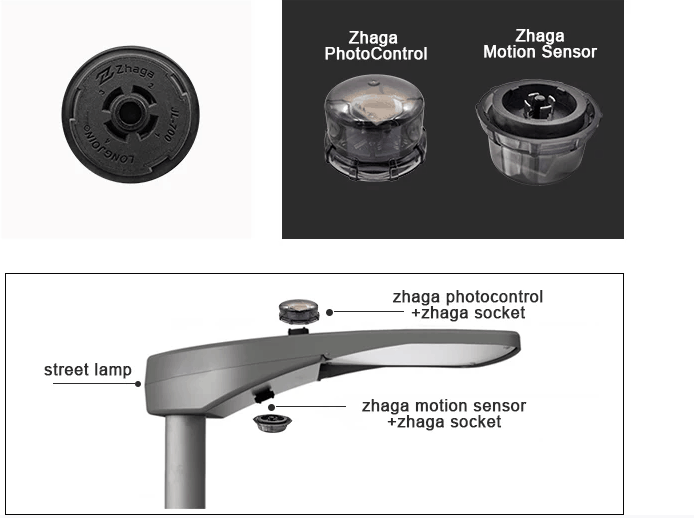
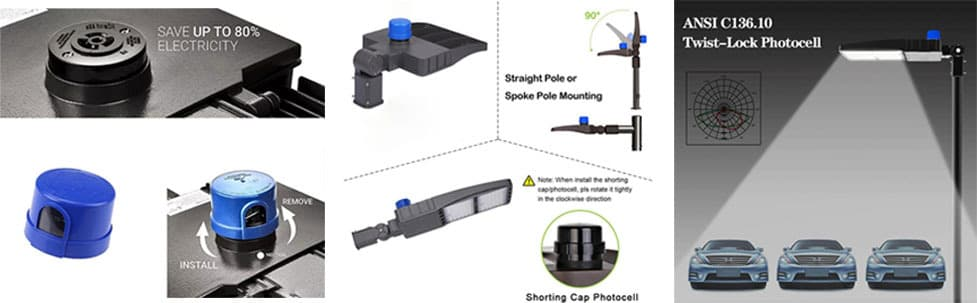
| Tipo de control | Compatible con enchufes con cable, con cierre giratorio o Zhaga |
| Rango de voltaje | 120–277 VCA (universal) |
| Características adicionales | Retardo de tiempo de apagado, protección contra sobretensiones, antiparpadeo |
Notas prácticas para seleccionar el modelo adecuado
- Umbrales de sensor:Utilice valores de lux de encendido más bajos en regiones con nubosidad frecuente, de modo que las luces no esperen demasiado para encenderse.
- Clasificación IP y durabilidadEn climas húmedos o polvorientos, elija modelos con clasificación IP65+ para resistir la penetración de agua. Muchas fotocélulas para exteriores tienen clasificación IP65.
- Interfaz de control:Si su sistema utiliza módulos Zhaga (comunes en sistemas LED avanzados), elija una fotocélula compatible con Zhaga para enchufarla directamente.
- Adaptación de voltajeVerifique siempre que el voltaje nominal de la fotocélula coincida con el de su circuito de iluminación. Las discrepancias pueden provocar fallos o mal funcionamiento.
- Protecciones adicionalesEl retardo de apagado evita la conmutación rápida ante condiciones de luz transitorias (p. ej., nubes, luces delanteras que pasan). La protección contra sobretensiones protege contra picos de tensión.
¿Cómo hacer? Sensores de fotocélula de luz ¿Mejorar los sistemas de iluminación inteligente?
Las fotocélulas actúan como nodos sensores dentro de un marco más amplio de iluminación inteligente. No solo encienden y apagan las luces, sino que también envían datos continuos de luz ambiental a sistemas de control de nivel superior.
Las modernas “fotocélulas inteligentes” ofrecen una respuesta más rápida y menos disparos falsos gracias a algoritmos mejorados de filtrado y detección.
Habilitación del control de iluminación adaptativa y por zonas
Sensor de luz Las entradas permiten que los sistemas de iluminación decidan qué zonas necesitan luz y en qué cantidad. Por ejemplo, atenuar las zonas periféricas mientras se mantiene la iluminación del área de juego.
En estadios, las fotocélulas ayudan a activar diferentes escenas (entrenamiento, partido, apagado) según la luz ambiental y la programación. Algunos fotocontroles admiten atenuación, no solo encendido/apagado, para permitir transiciones más fluidas.
Suministro de datos para algoritmos de iluminación
Las plataformas de control inteligente utilizan lecturas de luz ambiental de la interruptor de sensor de luz como entradas de referencia. Los algoritmos comparan esos datos con los niveles de lux objetivo para decidir si se debe reducir, mantener o aumentar la salida.
En sistemas con aprovechamiento de la luz natural, los datos de las fotocélulas garantizan que la iluminación eléctrica complemente la luz natural.
Trabajar con detectores de movimiento, infrarrojos y controles remotos
Las fotocélulas suelen estar conectadas a sensores de movimiento (PIR/IR). Esto garantiza que la iluminación esté apagada durante el día y que no haya movimiento.
En los nodos integrados, un solo dispositivo combina PIR + fotocélula + control de red para gestionar la regulación, la programación y las anulaciones remotas. Los controladores remotos o los paneles en la nube pueden anular o ajustar los puntos de ajuste, utilizando los datos de la fotocélula como referencia.
A continuación se muestra una comparación de los tipos de sensores utilizados con fotocélulas en un recinto deportivo.
| Tipo de sensor | Función | Beneficios en el control de la iluminación | Ejemplo de uso en recintos deportivos |
| Sensor de movimiento | Detecta movimiento | Activa las luces solo cuando es necesario | Pasarelas del campo de entrenamiento |
| Sensor de infrarrojos | Detecta el calor corporal | Mejora la precisión sobre el movimiento solo | Zonas de jugadores, áreas de asientos |
| Sensor de temperatura | Monitorea los cambios de calor | Admite iluminación adaptativa basada en el clima | Estadios cubiertos con climatización |
| Sensor acústico | Capta el ruido de la multitud | Activa efectos ambientales | Iluminación de celebración de goles |
¿Cuál es el futuro de? Controladores de alumbrado público ¿en recintos deportivos inteligentes?
Las fotocélulas están evolucionando: ya no serán simples detectores de luz. En los futuros espacios inteligentes, funcionarán como centros de sensores avanzados y conectados que coordinan múltiples entradas para un control más sofisticado.
Integración de múltiples sensores
sensores de luz Coexistirán y se fusionarán con sensores de movimiento, temperatura e infrarrojos. En lugar de activarse solo con la luz, los sistemas decidirán mediante múltiples señales (p. ej., presencia + luz + calor ambiental). Los sensores de nueva generación ya combinan esta fusión para ofrecer escenas de iluminación adaptativas.
Mejoras de precisión en la detección
Espere umbrales de sensibilidad más precisos y tiempos de respuesta más rápidos. El filtrado y los algoritmos avanzados reducirán los falsos positivos causados por cambios transitorios de luz (nubes, faros de automóviles). Estas mejoras contribuyen a que los sistemas de iluminación funcionen con mayor fluidez.
Aquí se muestran las métricas de rendimiento de las fotocélulas actuales frente a las de próxima generación.
| Parámetro | Rango actual | Capacidad emergente | Impacto |
| Sensibilidad (lujo) | 10–50 lux | 1–5 lux | Detecta cambios sutiles de luz. |
| Tiempo de respuesta | 1–2 segundos | <200 ms | Ajustes instantáneos |
| Tasa de activación falsa | 8–12% | <2% | Operación confiable |
| Esperanza de vida | 5–7 años | 10–12 años | Menor mantenimiento |
Compatibilidad con IoT
Fotocélulas Incorporará módulos de comunicación, es decir, LoRa, ZigBee, NB-IoT, que permiten:
- Monitoreo remoto
- Configuración
- Actualizaciones de firmware por aire
Uniones largas JL-245CZPor ejemplo, admite múltiples protocolos para una integración perfecta. El producto también cuenta con certificación internacional de ISO, CE, UL, y RoHS.
Marcos de iluminación que utilizan LoRaWAN Ya hemos demostrado cómo los controles pueden ahorrar energía a gran escala.
Aquí hay una tabla que describe algunos de los protocolos de comunicación más utilizados junto con su alcance, consumo de energía y aplicaciones adecuadas.

| Protocolo | Rango | Consumo de energía | Aplicación adecuada |
| ZigBee | 10–100 metros | Bajo | Estadios cubiertos |
| LoRaWAN | 2–5 km urbano, 15+ km rural | Muy bajo | campos al aire libre |
| NB-IoT | A escala nacional | Moderado | Iluminación deportiva en toda la ciudad |
| Wi-Fi 6 | <100 metros | Alto | Entornos de lugares con un alto nivel de datos |
Diseños de fotocélulas alimentadas por energía solar
Las fotocélulas pueden alimentarse directamente de módulos solares o circuitos de captación de energía. Esto las hace autosuficientes. En campos deportivos remotos o sin conexión a la red eléctrica, los sistemas de iluminación solar ya utilizan controladores autónomos.
Utilizando perovskita fotovoltaica o electrónica de potencia ultrabaja, las fotocélulas del futuro podrían funcionar sin cableado externo.
Palabras finales
Los recintos deportivos inteligentes exigen una iluminación precisa, adaptable y energéticamente eficiente. Las fotocélulas lo hacen posible gracias a un control inteligente basado en sensores. Para un rendimiento fiable, los fotocontroladores inteligentes LongJoin de Chi-Swear Son una opción confiable. Su durabilidad y calidad los convierten en un aliado sólido para proyectos de iluminación con visión de futuro.
Enlaces externos
- https://www.energystar.gov/sites/default/files/asset/document/Outdoor%20Area%20Lighting%20Papamichael.pdf
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lux
- https://www.iso.org/home.html
- https://single-market-economy.ec.europa.eu/single-market/goods/ce-marking_en
- https://www.ul.com/solutions
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RoHS
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s43926-025-00163-z
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zigbee
- https://lora-alliance.org/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Narrowband_IoT