Outline
- Introduction
- Understanding Photocells
- Energy Efficiency
- Reducing Light Pollution
- Carbon Footprint Reduction
- Cost Benefits
- Future Developments
- Final words
As the modern day cities are experiencing an exponential growth, the need for effective public lighting systems has never been more critical. This is mainly because, the conventional lighting techniques lag behind in sustainability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Consequently, cities are now prioritizing and implementing more ecological means of resisting climate change, and public lighting is at the heart of such transformations. Eco-friendly lighting systems, such as those utilizing smart sensors, offer a more efficient and environmentally conscious alternative.
By automatically adjusting to natural light levels, these light controllers reduce unnecessary energy use, promoting sustainability. Thus, they are becoming a key tool in the global shift towards sustainable urban lighting solutions. This article will discuss the environmental benefits of using light photocells in public lighting systems.
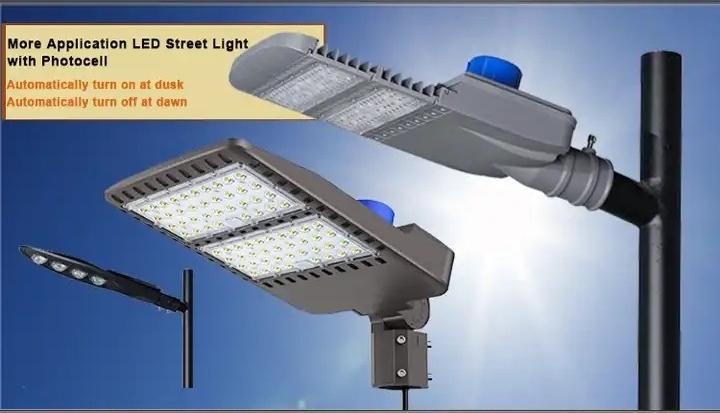

Understanding Photocells
Phtocells or photoelectric sensors are indispensable parts of modern-day smart lighting systems. They are designed to detect ambient light levels and automatically adjust artificial lighting accordingly.
Primarily manufactured from semiconductors like cadmium sulfide, their operation involves light conversion into electrical signals and relatively changing the intensity of light. In public lighting systems, they are commonly employed to turn on lights at dusk and off at dawn.
There are different types of these smart switches used in public lighting, however the most commonly available are: resistive, junction-based, and capacitive. Each type offers specific advantages for energy efficiency in different lighting environments.
- Resistive photocells adjust their resistance depending on the light intensity.
- Junction-based photocells, such as photodiodes, directly generate current when exposed to light.
- Capacitive photocells are more advanced, using electric fields to detect subtle changes in light.
Energy Efficiency
Light phtocells can effectively help enhance energy efficiency in public lighting. These devices ensure that streetlights are only on when necessary, reducing unnecessary energy use. By reacting to real-time changes in daylight, dusk-to-dawn sensors eliminate waste, particularly in the early morning or late evening when conventional lighting may stay on longer than needed.
For example, in San Sebastian, Spain, the integration of smart public lighting, which included photocells, led to a significant reduction in energy consumption. The project demonstrated how smart lighting infrastructure could reduce the city’s energy usage by as much as 80% while lowering maintenance costs due to more accurate on/off control.
Similarly, in Montreal, the switch from traditional lighting systems to a smart network utilizing lighting and LED fixtures contributed to a notable drop in electricity consumption, saving the city considerable costs while enhancing management capabilities.
Reducing Light Pollution

Light pollution is major concern in metropolitan across the globe. Smart light controls significantly reduce light pollution by turning lights on only when needed and adjusting brightness levels based on ambient light. By ensuring that public lighting is not excessively bright, they further help minimize light spills and preserve dark skies.
Tucson, Arizona, exemplifies this strategy. After the integration of 18,000 photocells for street light, the city reduced skyglow by 7%. This change lowered light pollution while maintaining energy efficiency. Other cities, like Pittsburgh and Copenhagen, have also adopted smart lighting technologies to cut down light pollution effectively.
Carbon Footprint Reduction
Carbon footprints go hand-in-hand with climate change, and the use of automatic light controllers could effectively help mitigate them. They adjust lighting, leading to a decrease in energy consumption and eventually lowering the demand for electricity and a subsequent reduction in carbon emissions.
For example, cities using photocells, such as Boston and Los Angeles, have reported significant energy savings, which translate to reduced greenhouse gas emissions. According to IEEE, smart lighting technologies, which often include photocells, can reduce energy usage by up to 70%, greatly impacting urban carbon footprints by minimizing the demand for power generation.
Globally, there are various initiatives that promote the use of smart switches and other smart lighting technologies. Programs like the European Commission’s lighting efficiency projects and India’s National Street Lighting Program have both focused on transitioning to energy-efficient lighting, reducing carbon emissions while simultaneously cutting energy costs.
Cost Benefits
Upgrading to photocell-based systems for public lighting presents significant long-term cost benefits. Apart from sustainability concerns, cities deploying these systems report less energy usage, lower operating costs, and higher ROI.
For example, with an LED street lighting project of 250,000 smart lights in New York City, it is estimated the city would save at least 14 million US dollars on annual energy and maintenance costs. The document also noted that such upgrades are worth considering as their payback period is less than six years.
Further, cities like Copenhagen and Chicago have also successfully integrated intelligent lighting systems, reducing costs through remote monitoring and predictive maintenance. Copenhagen’s adoption of adaptive streetlights has helped it achieve its goal of becoming carbon-neutral by 2025 while also significantly cutting down maintenance expenses.
The combination of decreasing energy and maintenance costs and the long lifespan of modern LEDs (up to 20 years) gives the assurance that the earliest expenditure incurred in the installation of photocell systems will yield returns in the long run.
Future Developments

The future of photocell technology lies in its integration with smart grids, AI, and IoT systems, enabling even more precise light management. Innovations like dynamic dimming and AI-driven lighting adjustments will optimize energy use further, responding in real-time to environmental conditions and urban activity.
Additionally, multi-spectral developments are expected, which can distinguish between different types of light pollution, further reducing unnecessary light emissions.
Urban areas envision integrating lighting control with other sustainable technologies, such as solar panels and smart networks, creating a holistic, energy-efficient infrastructure that promotes environmental conservation while reducing carbon footprints.
Final words
The integration of photocells into public lighting systems offers numerous environmental benefits, including energy savings, reduced carbon emissions, and minimized light pollution. As cities continue to prioritize sustainable urban development, photocell technology will remain crucial for eco-friendly lighting solutions. For reliable, high-quality photocell products, Chi-Swear is a trusted supplier, offering advanced technology to help cities achieve their sustainability goals.
External Links
- https://upcommons.upc.edu/handle/2117/355020
- https://www.dimonoff.com/resources/case-studies/city-of-montreal
- https://darksky.org/news/tucson-arizona-u-s-skyglow-reduced-7-after-street-light-conversion
- https://smartlighting.ieee.org/topics-ai/sml3-how-smart-lighting-saves-the-environment
- https://commission.europa.eu/projects/support-energy-efficient-street-lighting-systems_en
- https://eeslindia.org/en/ourslnp/
- https://smart-cities-marketplace.ec.europa.eu/sites/default/files/2021-06/Smart%20Lighting%20Factsheet_0.pdf