Outline
- Introduction
- How Big Data Works in Road Lighting?
- What Are The Impacts of Big Data on South American Cities? Case Studies
- What Are The Challenges Of Implementing Big Data?
- What Are The Benefits Of Using Big Data In The Management Of Urban Road Lighting?
- What Are The Emerging Trends in Big Data Analytics for Smart City Infrastructure?
- The Bottom Line
How can cities make road lighting smarter? Traditional streetlights waste energy and require frequent maintenance. But with big data, everything changes.
This allows cities to optimise their street lighting systems like never before. Primarily consisting of interconnected sensors, such as photocells, big data helps collect real-time data of various smart city components, ranging from street light scheduling to traffic flow, and environmental conditions.
This data-driven approach boosts efficiency, reduces operational costs, and enhances urban safety. Cities across the globe are rapidly adopting these innovations. In South America, this can be an effective tool in the smart management of urban road lighting.

How Big Data Works in Road Lighting?
In smart cities working of Big Data is a three-step process.
- Installation of smart photo controllers with other sensors.
- Collection of real-time data.
- Transmission of data to make changes accordingly.
However, regarding sensors, they can vary depending on a municipality’s needs. For instance, photocells coupled with IR sensors and cameras can detect traffic flow and pedestrian movement, making changes in ambient light levels accordingly.
A Big Data-enabled system was implemented in Oslo in 2006. Its two basic features include:
- Cameras and photocell sensors to monitor real-time conditions
- Technology advanced lights that can communicate with each other
The project has yielded many tangible benefits. The system brightens when sensing activity and dims when there’s none. This led to significant energy savings and improved roadway safety.
What Are The Key Metrics Needed To Optimize Road Lighting Systems?
This relies on the collection and analysis of specific data points. Here’s the table summarizing their details.
| Metric | Description |
| Traffic Flow Data | Tracks vehicle and pedestrian movement to adjust lighting based on real-time usage. |
| Energy Consumption Metrics | Monitors the energy usage of each lighting unit to detect inefficiencies and optimize performance. |
| Environmental Conditions | Considers weather and natural light levels to dynamically adjust brightness for consistent illumination. |
| Operational Status | Provides real-time data on lighting functionality to enable proactive maintenance and reduce downtime. |
By systematically analyzing these data points, municipalities can implement adaptive lighting strategies. This structured approach will ensure improved energy efficiency and urban safety.
What Are The Impacts of Big Data on South American Cities? Case Studies
Many successful cases can be analysed to gauge the impact of Big Data coupled with outdoor lighting. Below are some examples in this regard.
São Paulo, Brazil
The project aimed to revitalise the Pinheiros River area in São Paulo. Its primary features include:
- Installation of 628 smart lighting points along a 14 km cycling trail.
- Solar Trees to be used as a source of renewable energy for LED lights.
- Charging stations for electronic devices are provided throughout the route.
What were the impacts? This integration of smart lighting and renewable energy has transformed the area into Brazil’s first smart cycling trail.
Buenos Aires, Argentina
This program was launched in cooperation with Philips. The details are:
Key Features
- Upgrade of 91,000 streetlights to LED technology
- ICT solution for remote monitoring and control of 72% of streetlights
- Individual light point monitoring for optimised operation and maintenance
Outcomes
- 50% reduction in emissions
- 60% monetary savings
- Improved energy efficiency and maintenance scheduling
Santiago, Chile
The city entered a 15-year agreement with ENGIE to modernise and manage its public lighting. To accommodate Santiago’s complex urban landscape, this project utilized communication protocols such as LoRaWAN in deploying photo controllers. As a result, both energy consumption and maintenance costs witnessed significant cuts.
Nobsa, Colombia
The municipality of Nobsa combined LoRa and GSM technologies to establish a reliable private network, integrating 605 pole-mounted controllers. Features include:
- Autonomous operation based on predefined astronomic calendars
- Remote ON/OFF
- Dimming control
This initiative improved lighting awareness, reduced pollution, conserved energy, and enhanced street safety, while also accommodating community events.
What Are The Challenges Of Implementing Big Data?
Integration with Existing Infrastructure

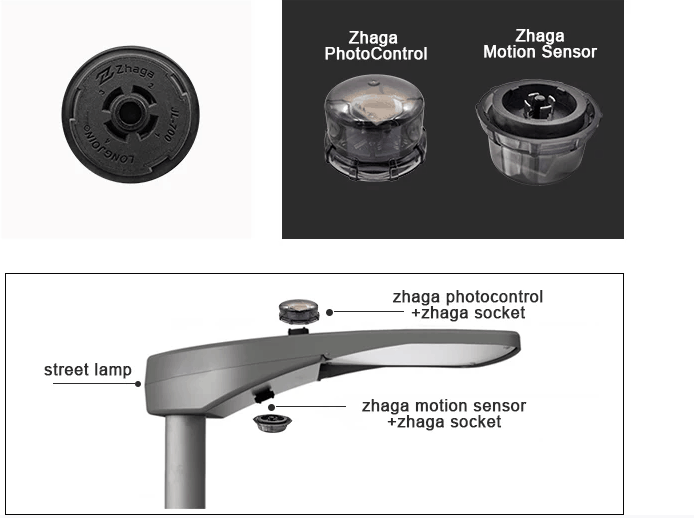
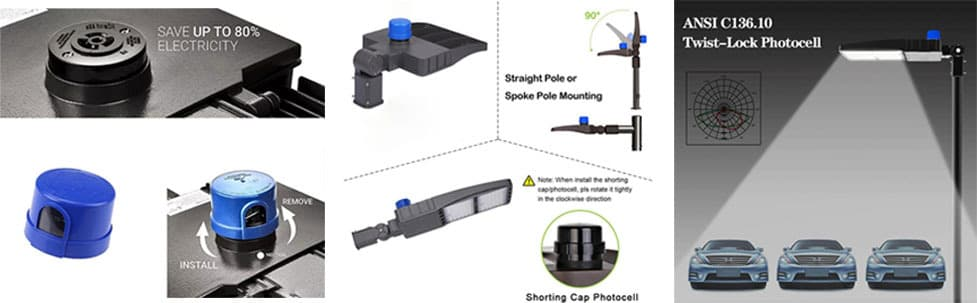
Upgrading to smart lighting systems requires compatibility of new technologies with existing infrastructure. This can be challenging. However, photocells, like those of LongJoin’s, could be a way forward for seamless integration with the city’s diverse urban landscape. They follow international protocols like ANSI and are also compatible with communication technologies like Zigbee and LoRaWAN.
Data Management and Analysis
Big Data involves the combined work of photocells with multiple other sensors. They can pose challenges in terms of data storage, processing, and analysis. To tackle this, many smart platforms like Signify’s Interact City are available. They facilitate efficient data handling and informed decision-making.
Financial Investment and Sustainability
Overhauling traditional lighting with their smart options requires hefty initial investments. While ROI’s are significant, these upfront costs could be a serious concern. The way forward depends on financial conditions and the goals of municipalities. For example, Rio de Janeiro demonstrated a model where operational costs were lowered and the pre-existing public lighting tax was used.
While the above-given challenge could have serious financial impacts, another challenge is the public acceptance. Awareness campaigns could be helpful in this regard.
What Are The Benefits Of Using Big Data In The Management Of Urban Road Lighting?
The table below highlights the efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and safety benefits of data-driven smart lighting systems.
| Benifits | Real World Example |
| Energy Consumption Reduction | Copenhagen: Adaptive lighting achieves ~50% energy savings.Chicago: Replacing 85% of public lights is projected to lower energy consumption by 50-75%. |
| Maintenance Cost Savings | Joondalup, Australia: Featured IoT enabled smart LED street lighting, leading to a 65% reduction in energy bills and better infrastructure control. |
| Enhanced Public Safety | Singapore: Intelligent streetlights optimize brightness based on pedestrian and vehicular activity.New York: Smart street lighting improved safety, lighting quality, and reduced costs. |
What Are The Emerging Trends in Big Data Analytics for Smart City Infrastructure?

Integration of AI and IoT
The confluence of AI with the IoT is revolutionizing how cities used to be managed. Now, AI algorithms can process vast data from IoT devices. This enables predictive analytics for urban planning and resource allocation. Operational efficiency in urban environments and improved decision-making are some crucial outcomes of this convergence.
Adoption of 5G Connectivity
Communication is the backbone of smart city initiatives. 5G’s ultra-fast speed and low latency are making real-time data transmission possible. This will advance the application of real-time monitoring in improving public service delivery.
Emphasis on Data Governance and Ethics
In the tech-enabled age today, spyware remains a persistent threat. As data collection intensifies, cities are concentrating their efforts. Strong data governance will ensure ethical use of information and will foster public trust in smart city initiatives.
The Bottom Line
Smart management of urban road lighting in South America shows how big data-driven solutions can help municipalities. As cities continue adopting intelligent lighting systems, choosing reliable components is key. Chi-Swear’s advanced light controllers ensure seamless integration and long-term performance, making them a trusted partner in the evolution of smart urban lighting.
External Links
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intelligent_street_lighting
- https://corporate.enelx.com/en/media/case-studies/2022/06/smart-public-lighting-sao-paulo
- https://unfccc.int/climate-action/momentum-for-change/activity-database/momentum-for-change-replacement-of-the-street-lighting-system-with-led-technology
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LoRa
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GSM
- https://www.ansi.org/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zigbee